


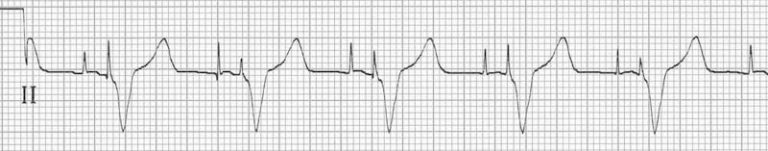
Medical uses for this information are varied and often need to be combined with knowledge of the structure of the heart and physical examination signs to be interpreted. The overall goal of performing an ECG is to obtain information about the electrical functioning of the heart. Ī 12-lead ECG of a 26-year-old male with an incomplete right bundle branch block (RBBB) Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of heart drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. ĭuring each heartbeat, a healthy heart has an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads throughout the atrium, and passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers, spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. There are three main components to an ECG: the P wave, which represents depolarization of the atria the QRS complex, which represents depolarization of the ventricles and the T wave, which represents repolarization of the ventricles. In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle.
The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles ("leads") and is recorded over a period of time (usually ten seconds). In a conventional 12-lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. However, other devices can record the electrical activity of the heart such as a Holter monitor but also some models of smartwatch are capable of recording an ECG.ĮCG signals can be recorded in other contexts with other devices. Traditionally, "ECG" usually means a 12-lead ECG taken while lying down as discussed below. Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances (such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia ), inadequate coronary artery blood flow (such as myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction ), and electrolyte disturbances (such as hypokalemia and hyperkalemia ). These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. Use of real time monitoring of the heart in an intensive care unit in a German hospital (2015), the monitoring screen above the patient displaying an electrocardiogram and various values of parameters of the heart like heart rate and blood pressureĮlectrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram ( ECG or EKG ), a recording of the heart's electrical activity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
